Python环境搭建 下载地址:https://www.python.org/
安装步骤
(1)选择自定义安装,勾选添加到Path环境变量
(2)默认即可,点击next
(2)选择软件安装位置,点击install
测试
打开命令行窗口,输入python,显示如下,则python环境搭建成功
Flask项目部署 操作系统:Ubantu20
阿里云默认安装mysql8.0版本,python3.8
1.1安装nginx 更新安装源
1、sudo apt update
安装nginx
2、apt install nginx
换源安装MySQL5.7
1 cp /etc/apt/sources.list /etc/apt/sources.list.bak
编辑/etc/apt/sources.list
镜像地址
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 deb http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu/ xenial main restricted universe multiverse
更新安装源
1.2安装Mysql mysql 安装
1 sudo apt install mysql-server mysql-client
安装memcache
更新pip
1 pip3 install --upgrade pip
安装虚拟环境管理包
1 pip install virtualenvwrapper
虚拟环境配置
1 2 3 export WORKON_HOME=$HOME/.virtualenvs
执行命令
创建虚拟环境
1 mkvirtualenv --python=/usr/bin/python3 dxzlk_env
1.3安装uwsgi 安装uwsgi
路径:/srv/dazlk/uwsgi.ini
配置uwsgi
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 [uwsgi] # 项目的路径 # Flask的uwsgi文件 # 回调的app对象 # Python虚拟环境的路径 # 进程相关的设置 # 主进程 # 最大数量的工作进程 # http = :5000 监听5000端口(或监听socket文件,与nginx配合) # 设置socket的权限 # 退出的时候是否清理环境
1.4nginx配置 nginx配置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 upstream dxzlk{# 配置服务器
测试nginx
1 service nginx configtest
重启nginx
nginx 常用命令
1 2 3 4 启动:service nginx start
启动运行uwsgi
使用supervisor管理uwsgi进程
安装supervisor
配置文件:/srv/etc/dxzlk/supervisor.conf
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 # upervisor的程序名字 # supervisor执行的命令 # 项目的目录 # 开始的时候等待多少秒 # 停止的时候等待多少秒 # 自动开始 # 程序挂了后自动重启 # 输出的log 文件 # 输出的错误文件 # log 的级别# supervisor的服务器 # 用户名和密码 # 使用supervisorctl的配置 # 使用supervisorctl登录的地址和端口号 # 登录supervisorctl的用户名和密码
启动supervisor
1 supervisord -c supervisor.conf
通过supervisor客户端查看进程
1 supervisorctl -c supervisor.conf # 进入到管理控制台
supervisor 常用明令
1 2 3 4 5 6 status # 查看状态
Python闭包 闭包(Closure)是指在一个函数内部定义的函数,并且该内部函数可以访问外部函数的变量。闭包可以捕获并保持外部函数的状态,即使外部函数已经执行结束,内部函数仍然可以访问和操作外部函数的变量。
在Python中,定义闭包的一般形式是在一个函数内部定义另一个函数,并将内部函数作为返回值返回。内部函数可以访问外部函数的局部变量,并且可以在外部函数执行完毕后继续访问和修改这些变量。
以下是一个简单的示例,展示了闭包的用法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 def outer_function (x ):def inner_function (y ):return x + yreturn inner_function10 ) 5 ) print (result)
在上面的示例中,outer_function是外部函数,它接受一个参数x。在outer_function内部,定义了内部函数inner_function,它接受另一个参数y,并返回x + y的结果。outer_function最后将inner_function作为返回值返回。
通过调用outer_function(10),我们得到一个闭包closure,它实际上是一个函数,可以在后续的代码中使用。当我们调用closure(5)时,实际上是调用了内部函数inner_function,并将x的值设置为10,y的值设置为5,返回结果15。
本篇文章主要介绍python程序的执行机制
Python字节码 1.不含import语句的源代码 main.py
执行main.py
不会生成字节码文件main.pyc
2.含import语句的源代码 main.py
1 2 import utilsprint ('main' )
utils.py
1 2 3 def add (n1, n2 ):return n1 + n2print ('utils' )
执行mian.py脚本,会生成字节码文件utils.cpython-38.pyc
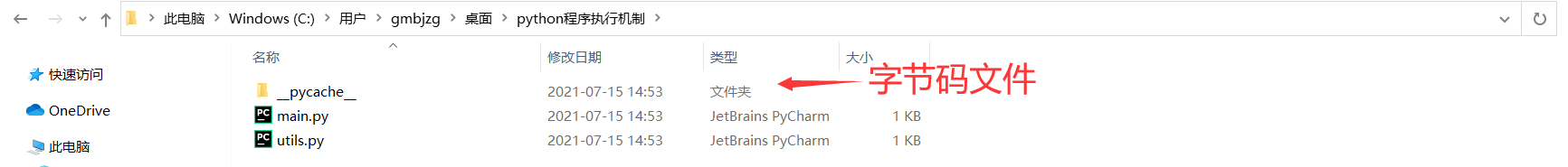
文件目录结构
树形结构如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 C:.
字节码文件可以直接被python解释器执行
3.结论 python源代码经过先编译生成字节码,再加载字节码到内存中执行,.pyc文件可以提高程序的执行效率。如果源代码不包含import语句,main.py先编译生成字节码,再加载到内存中执行。但不会做持久化存储,生成main.pyc字节码文件。
Python多进程 多进程
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 import multiprocessing
参数传递
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 import multiprocessing
守护进程
主进程执行结束,子进程也结束运行
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 import multiprocessing
进程通信
Windows
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 import multiprocessing
Python结构化时间 示例代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 time int (time.time())print (time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S" ,struct_time))
面向对象 类的定义
对象的创建
类属性
1 2 3 class Person:
方法
区别:方法第一个接收的参数不同
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Person:
继承
1 2 3 4 5 6 class Animal:
对象实例化初始操作
1 2 3 class Person:
七牛云存储 1、后台接口编写
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @app.route('/uptoken/' def uptoken ():'Uxv7S8cYoVvzznmVcWegxzV-ihWvqjDR5iV3Joph' 'jM_VBuv9TODxZ0M1F5hPUtYkyGhjutKQXzRSe93Q' 'dxzlk' return {"uptoken" : token}
2、前端上传接口编写
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 <!DOCTYPE html>"en" >"UTF-8" >"https://cdn.staticfile.org/Plupload/2.1.1/moxie.js" ></script>"https://cdn.staticfile.org/Plupload/2.1.1/plupload.dev.js" ></script>"https://cdn.staticfile.org/qiniu-js-sdk/1.0.14-beta/qiniu.js" ></script>"{{ url_for('static',filename='gmqiniu.js') }}" ></script>id ="upload-btn" >上传文件</button>input type ="text" id ="image-input" >"" alt="" id ="img" >'domain' : 'http://gmbjzg.top/' ,'browse_btn' : 'upload-btn' ,'uptoken_url' : '/uptoken/' ,'success' : function (up,file,info) {'image-input' ).value = url;
注意事项:绑定自已的域名需要在域名提供商添加一条CNAME记录
虚拟环境 (1)安装依赖
1 pip install virtualenvwrapper-win
(2)创建虚拟环境
(3)激活虚拟环境
(4)退出虚拟环境
(5)删除虚拟环境
(6)列出所有虚拟环境
注:虚拟环境默认安装在用户下的Envs文件夹