算法引入 a + b + c = 1000 且 a^2 + b^2 = c^2,求出 a, b,c所有组合结果
思想:枚举法,列出所有可能结果
1 2 3 4 5 for a in range (1001 ):for b in range (1001 ):for c in range (1001 ):if a + b + c == 1000 and a**2 + b**2 == c**2 :print (a, b, c)
优化
1 2 3 4 5 for a in range (1001 ):for b in range (1001 ):1000 - a - bif a**2 + b**2 == c**2 :print (a, b, c)
算法衡量 时间复杂度 :程序的执行步骤
大O表示法 :忽略常数项和次要项
最坏时间复杂度: 程序最多执行多少个步骤
常见时间复杂度
注:
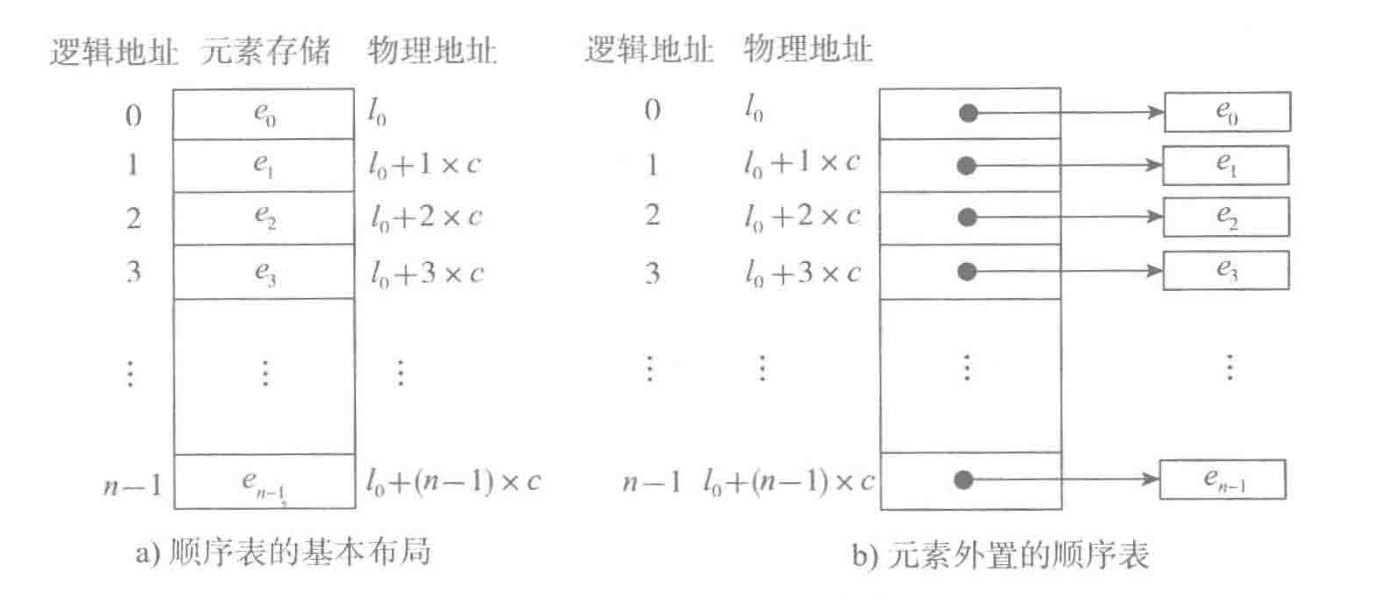
顺序表
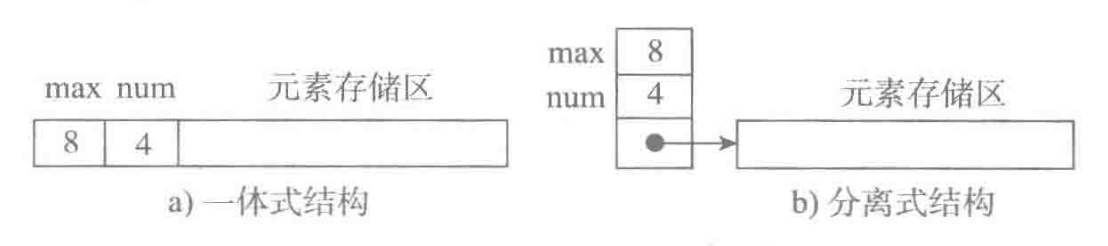
顺序表的两种基本实现方式 顺序表包含表头信息 和元素存储区 两部分
元素存储区扩充 两种扩充策略
每次扩充增加固定数目的存储位置,如每次扩充增加10个元素位置
每次扩充容量加倍,如每次扩充增加1倍存储空间
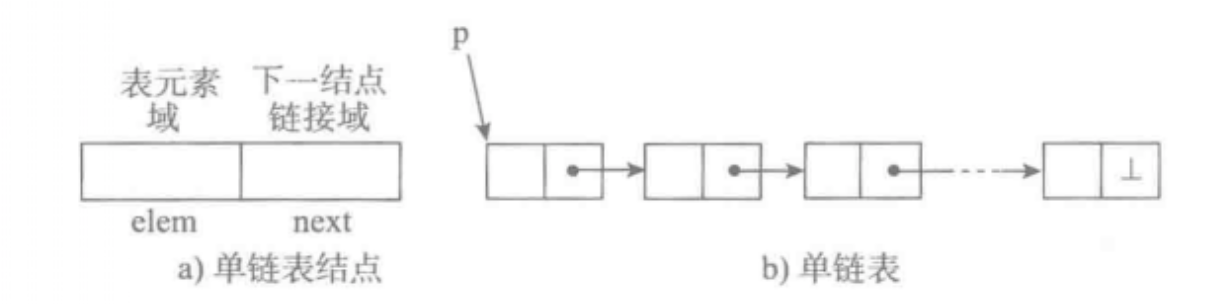
单链表
节点定义 1 2 3 4 class Node :__init__ (self, val):val = valnext = None
单链表的定义 1 2 3 class SingleLinkList :__init__ (self, node=None ):header = node
单链表操作 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 class Node :__init__ (self, val):val = valnext = None class SingleLinkList :__init__ (self, node=None ):header = nodeis_empty (self):return self.header == None length (self):header 0 while current != None :1 next return counttravel (self):header while current != None :print (current.val )next append (self, val):header if current == None :header = Node (val)else :while current.next != None :next next = Node (val)add (self, val):Node (val)if self.header == None :header = nodeelse :next = self.header header = nodeinsert (self, pos, val):Node (val)header if pos == 0 :next = currentheader = nodelength ():append (val)else :0 while current_pos != pos - 1 :1 next next = current.next next = noderemove (self, val):None header while current.val != val :next if pre == None :header = current.next else :next = current.next search (self, val):header while current != None :if current.val == val :return True next return False SingleLinkList ()append (1 )append (2 )append (3 )add (5 )insert (1 , 100 )remove (2 )print (s.travel ())print (s.search (5 ))
单向循环链表 双向链表 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 class Node :def __init__ (self, val ):next = None None class DoubleLinkList :def __init__ (self, node=None ):def travel (self ):while current != None :print (current.val)next def append (self, val ):if current == None :else :while current.next != None :next next = nodedef add (self, val ):if self.header == None :else :next = self.headernext .prev = nodedef insert (self, pos, val ):if pos == 0 :next = currentnext .prev = nodeelif pos >= self.length():else :0 while current_pos != pos:1 next next = currentnext = nodedef remove (self, val ):while current != None :if current.val == val:if current.prev is None :if current.next is not None :next next .prev = None else :None elif current.next is None :next = None else :next = current.next next .prev = current.prevnext 1 )2 )3 )0 , 6 )2 )
栈 栈的数据结构实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Stack :def __init__ (self ):def push (self, item ):def pop (self ):return self.container.pop()def peek (self ):return self.container[-1 ]def size (self ):return self.size()def is_empty (self ):return not self.container1 )2 )print (s.is_empty())
队列 java代码实现
python代码实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Queue :def __init__ (self ):def enQueue (self, val ):0 , val)def deQueue (self ):return self.container.pop()def isEmpty (self ):return not self.containerdef size (self ):return len (self.container)1 )print (q.deQueue())
树
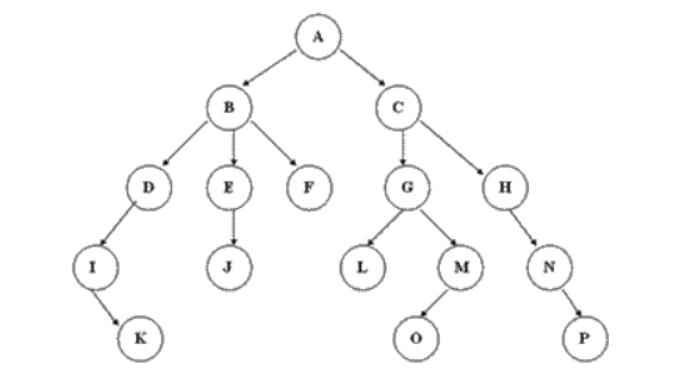
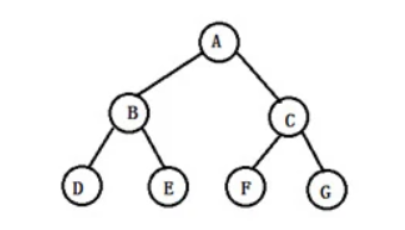
树结构是一种非线性存储结构,存储的是具有“一对多”关系的数据元素的集合。每一个非空树都有且只有一个被称为根的结点
基本概念
(1)节点的度 :一个节点含有的子树的个数称为该节点的度
如A节点的度为2、B节点的度为3
(2)树的度 :一棵树中,最大的节点的度称为树的度
如上面这棵树的度为3
(3)叶子节点 :度为0的节点
如K、F、O、P等都是叶子节点
(4)节点的层次 :从根开始定义起,根为第1层,根的子节点为第2层
上面这颗树一共有5层
(5)树的高度或深度 :树中节点的最大层次
上面这颗树的高度或深度为5
(6)森林 :由m(m>=0)棵互不相交的树的集合称为森林
二叉树 二叉树 :每个节点最多含有两个子树的树称为二叉树
几个性质
(1)在二叉树的第
(2)深度为
(3)对于任意一棵二叉树,如果其叶结点数为
(4)具有
(5)对完全二叉树,若从上至下、从左至右编号,则编号为i的结点,其左孩子编号必为
完全二叉树 设二叉树的高度为h,除第 h 层外,其它各层 (1~h-1) 的结点数都达到最大个数,第h层有叶子结点,并且叶子结点都是从左到右依次排布,这就是完全二叉树
满二叉树
平衡二叉树 当且仅当任何节点的两棵子树的高度差不大于1的二叉树
排序二叉树 从根节点按照编号,从左到右进行编号
2-3-4树 红黑树 B树 霍夫曼树 遍历 前序、中序、后序
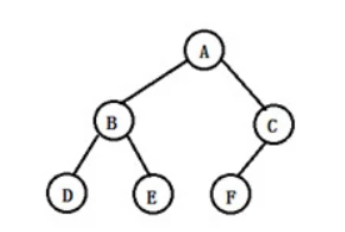
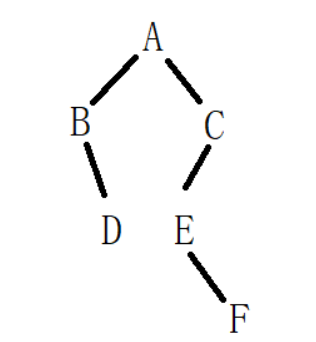
依据前序和中序或者前序和后序可以完整的构建出一颗二叉树
前序:A B D C E F
中序:B D A E F C
(1)确定根A
(2)依据中序A所在位置划分左右两颗子树
后序:D B F E C A
中序:B D A E F C
(1)确定根的位置A
(2)依据中序划分左右两颗子树
冒泡 思路分析
比较前后两个数, 如果前面一个数比后面一个数大, 则交换位置。
python示例代码如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 arr = [1 , 100 , 35 , 56 , 72 , 5 , 3 , 2 ]def bubble_sort (arr ):"""冒泡排序""" len (arr) - 2 )while j != 0 :0 0 while i != j:if arr[i] > arr[i+1 ]:1 ] = arr[i+1 ], arr[i]1 1 if arr[i] > arr[i+1 ]:1 ] = arr[i+1 ], arr[i]1 if flag == 0 :return 1 print (arr)
java版本示例代码如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public class HelloWorld {public static void main (String[] args) {int [] arr = {1 , 5 , 2 , 7 , 9 };int len = arr.length;for (int j=len-1 ; j>=2 ; j--){for (int i=0 ; i<j; i++){if (arr[i] > arr[i+1 ]){int temp = arr[i + 1 ];1 ] = arr[i];for (int i=0 ; i<len; i++){
选择 思路分析
打擂台算法,每次都找到最大值或最小值, 与数组最后一个元素交换位置。
python示例代码如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 arr = [4 , 100 , 35 , 56 , 72 , 5 , 3 , 1 ]def select (arr ):"""选择排序""" 0 while j != (len (arr) - 1 ):1 while index != (len (arr) - 1 ):if arr[min_index] > arr[index]:1 if arr[min_index] > arr[index]:1 print (arr)
java代码示例如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 public class HelloWorld {public static void main (String[] args) {int [] arr = {1 , 100 , 2 , 7 , 9 };int len = arr.length;for (int j=len; j>=2 ; j--){int maxIndex = 0 ;for (int i=1 ; i<j; i++){if (arr[i] > arr[maxIndex]){if (maxIndex != j-1 ){int temp = arr[j - 1 ];1 ] = arr[maxIndex];for (int i=0 ; i<len; i++){
插入 示例代码如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 arr = [100 , 4 , 35 , 23 , 72 , 5 , 3 , 1 ]def insert_sort (arr ):"""插入排序""" 1 while index != len (arr):while start != 0 :if arr[start] < arr[start - 1 ]:1 ] = arr[start - 1 ], arr[start]1 1 print (arr)
二分 java示例代码如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 package com.cskaoyan;import java.util.Scanner;class Demo {int [] arr = {1 , 4 , 11 , 18 , 19 };int index = binarySearch(arr, 17 );int binarySearch(int [] arr, int num){int left = 0 ;int right = arr.length - 1 ;int mid = (left + right) / 2 ;while (true){if (arr[mid] == num){return mid;if (arr[mid] > num){1 ;else {1 ;2 ;if (left > right){return -1 ;
数字累加 计算1到100之和
循环
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public static int sum (int n) {int sum = 0 ;for (int i=1 ; i<=n; i++){return sum;
其他解法
1 2 3 public static int sum (int n) {return (1 + n) * n / 2 ;
斐波那契 0 1 1 2 3 5 8 13
求第n个斐波那契数列的值
递归
1 2 3 4 5 6 public static int fio (int n) {if (n <= 2 ){return n - 1 ;return fio(n-1 ) + fio(n-2 );
循环
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public static int fio (int n) {if (n <= 2 ){return n - 1 ;int first = 0 ;int second = 1 ;for (int i=0 ; i<n-2 ; i++){int sum = first + second;return second;
从上到下打印二叉树 示例代码如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) return new ArrayList ();new ArrayList ();new LinkedList ();boolean isOdd = false ;while (!queue.isEmpty()){int size = queue.size();new LinkedList ();for (int i=0 ; i<size; i++){TreeNode node = queue.poll();if (isOdd){else {if (node.left != null ){if (node.right != null ){return arrayList;
从上到下打印二叉树
示例代码如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) return new ArrayList ();new ArrayList ();new LinkedList ();while (!queue.isEmpty()){int size = queue.size();new ArrayList ();for (int i=0 ; i<size; i++){TreeNode node = queue.poll();if (node.left != null ){if (node.right != null ){return listArray;
示例代码如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 class Solution {public int [] levelOrder(TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) return new int [0 ];new ArrayList ();new LinkedList ();while (!queue.isEmpty()){TreeNode node = queue.poll();if (node.left != null ){if (node.right != null ){int [] res = new int [arrayList.size()];int index = 0 ;for (Integer i : arrayList){return res;
只出现一次字符 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution {public char firstUniqChar (String s) {new HashMap ();for (int i=0 ; i<s.length(); i++){char c = s.charAt(i);if (!hashMap.containsKey(c)){1 );else {int val = hashMap.get(c);1 );for (int i=0 ; i<s.length(); i++){char c = s.charAt(i);if (hashMap.get(c) == 1 ){return c;return ' ' ;
二维数组 示例代码如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution {public boolean findNumberIn2DArray (int [][] matrix, int target) {int row = matrix.length - 1 ;int column = 0 ;while (row >= 0 && column < matrix[0 ].length){if (matrix[row][column] == target){return true ;if (matrix[row][column] > target){else {return false ;